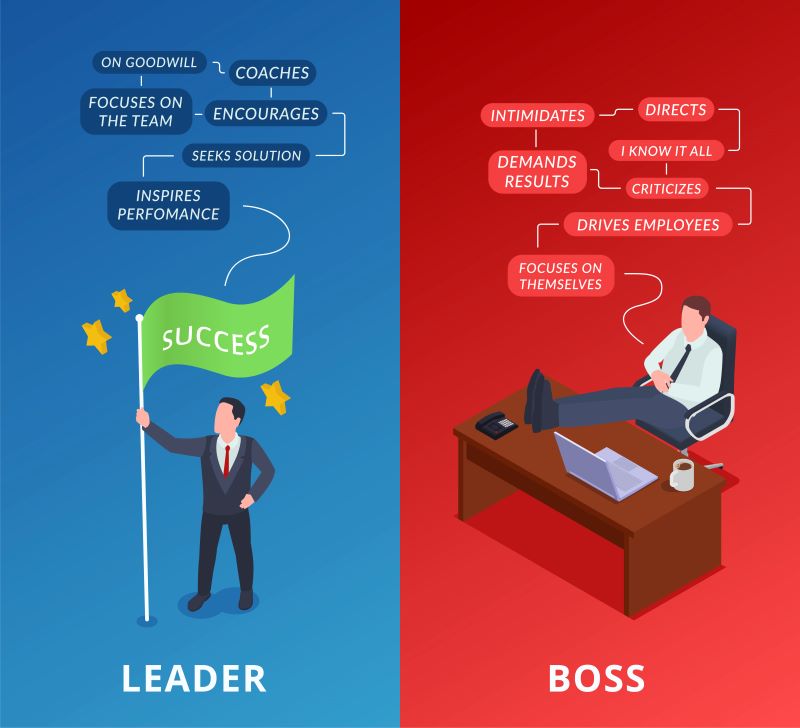
Unlocking the Tapestry of Leadership styles in Management
Leadership is a multifaceted and dynamic concept that incorporates an extensive array of strategies and methods. Understanding these categories and styles of leadership is essential for both personal and professional growth. This blog seeks to explore the multifaceted nature of leadership, encompassing its diverse aspects, types, and significance across a range of contexts.
The Essence of Leadership and Leadership Styles
Leadership is essentially about inspiring, motivating, and guiding individuals or groups towards a shared goal. To be an effective leader, you must have the flexibility to apply several leadership philosophies depending on the situation and the requirements of your team. These various leadership theories and methods cover different situations and group dynamics.

Exploring Leadership Types and Styles
The landscape of leadership is extensive and varied. Few most renowned leadership styles:
1. Autocratic Leadership:
Autocratic leaders want their teams to obey their orders without question and make judgements on their own. This strategy is useful in circumstances that call for quick decisions. Nevertheless, it can also hinder creativity and creative thinking, which over time leads to alienation and high employee turnover rates.
2. Authoritative Leadership:
Authoritative leadership is exemplified by leaders who present a compelling vision and purpose, thereby inspiring their teams. They provide direction and encourage team members to take initiative within the context of the larger vision.
3. Transformational Leadership:
Change agents are transformational leaders. Their compelling vision inspires and motivates their teams and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. This methodology is extraordinarily beneficial in innovative and dynamic work environments.
4. Situational Leadership:
Situational leaders adapt their approach to persuasion based on the specific circumstances and performance requirements of their team. Because of their adaptability, they can effectively respond to both individual and group needs in a variety of contexts.
5. Transactional Leadership:
Transparent Expectations and Processes are the emphasis of transactional leaders. To encourage adherence to the specified norms and performance, they use rewards and penalties.
6. Trait Leadership:
This view holds that certain individuals are naturally superior leaders due to their possession of particular personality traits, such as intelligence, charisma, and self-assurance. However, in addition to these qualities, other elements can affect a leader’s performance.
7. Servant Leadership:
Servant leadership entails prioritizing the requirements and personal growth of team members. They establish a supportive and cooperative work atmosphere by being empathic, paying close attention when others are speaking, and supporting their teams.

Autocratic Leadership: Qualities and Application
They autonomously form judgements and expect unquestioning compliance from their team. This leadership style is highly effective in emergency crises and other circumstances that demand prompt and resolute action. However, this could potentially stifle creativity and innovation, resulting in decreased employee engagement.
Authoritative Leadership:
Characteristics of an authoritarian leader include the following:
– Decisiveness
– Efficiency
– High Level of Control
– Low Team Involvement
Transformational Leadership: Qualities and Application
Transformational leaders are characterized by their inspirational and forward-thinking methodology. They motivate their teams to accomplish ambitious goals by leading by example. This particular approach proves to be highly effective in organizations that prioritize innovation and adaptability, as it fosters the creative thinking and individual growth of team members.
The following are characteristics of a transformational leader:
– Charming
– Vision – Authorization
– Promotes innovation and change
Situational Leadership: Adapting to Context
Situational leaders possess an awareness of the importance of modifying their strategy in accordance with particular conditions. Through the assessment of their team members’ readiness and competencies, situational leaders possess the ability to adapt their strategy accordingly. Their capacity for adaptability empowers them to thrive in an array of situations.
Transactional Leadership: Emphasis on Structure
Transactional leaders prioritize structure, processes, and adherence to established standards to a considerable extent. Reward and punishment are used to motivate and control the team. This tone is appropriate for environments where explicit expectations and consistent procedures are crucial, such as manufacturing or administrative positions.
Democratic Leadership: Prioritizing Well-Being
A democratic leader prioritizes the health and development of his or her team members. They proactively address the needs of their team members and foster their development on both a personal and professional level. This strategy fosters team collaboration, trust, and a sense of community.
Discovering Your Leadership Style
Consider the following actions to determine your leadership style:
1. Self-Evaluation: Reflect upon your previous leadership experiences and inherent inclinations. Which of the following best describes your personality type: rule-maker, team builder, or visionary?
2. Feedback Request the input of your superiors, subordinates, and colleagues. They can offer insightful information on your management style and how it affects the team.
3. Education and Training: Engage in leadership development programmes, seminars, or coaching sessions. Discovering your preferences and opportunities for development can be aided by learning about various leadership types and styles.
4. Trial and error: Experiment with several leadership philosophies in a range of circumstances. To improve your strategy, take lessons from your triumphs and mistakes.
5. Self-reflection: Regularly evaluate the outcomes of your leadership experiences. Analyze what went well and what may be done better.
Unlock Top Talent Today! Join IDJF for the Best Candidates!

Leadership Styles in Management
The significance of leadership styles in management is paramount across diverse contexts:
1. Effective project management: The achievement of effective project management often necessitates the integration of situational and transformational leadership styles. In addition to motivating their teams, project managers must be able to adjust to changing project requirements.
2. The application of servant leadership in team management yields several benefits, including the promotion of trust, collaboration, and a collective concern for the team’s welfare.
3. Crisis Management: An authoritative or autocratic leadership style may be necessary to ensure control and make prompt, decisive decisions during times of crisis.
4. Change Management: The implementation of organizational changes requires the presence of transformational leadership. It is the duty of leaders to inspire and enable their teams to adapt to change.
In conclusion, leadership is a dynamic and multifaceted concept with a variety of types and approaches. The most effective leaders can adapt their approach to meet the needs of the moment, their team, and the circumstance. One can enhance their leadership influence in any professional environment by identifying and developing their distinct leadership style and consistently honing their abilities. Whether your objective is to exert influence, lead with authority, or serve your team, embracing and honing your personal leadership style is critical to your success.