Gender Inequality: Meaning, Cause and Solutions
Gender inequality is a common issue that goes beyond geographical, cultural, and socio-economic boundaries. It includes differences between men and women in terms of opportunities, resources, and rights. The purpose of this blog is to explain what gender inequality means, look into its causes, and talk about possible ways to make society more equitable.
Gender inequality refers to the unfair and unequal treatment of people based on their gender. This can manifest in many ways, including:
- Discrimination can result in individuals being denied opportunities, receiving lower pay than their male counterparts for performing the same work, or experiencing physical abuse or harassment.
- Stereotyping occurs when individuals are expected to possess specific traits or skills based on their gender. Women may be stereotyped as emotional or weak, while men may be stereotyped as powerful or aggressive.
- Subordination occurs when one gender is considered less important than the other. As a result, women may be excluded from decision-making processes or subjected to mistreatment.
Gender inequality has far-reaching consequences for both men and women. It can also lead to poor health, violence, and hunger. It can also keep people from doing what they’re really capable of.
The Meaning of Gender Inequality
Gender inequality refers to the unequal treatment or representation of individuals based on their gender. Differences in education, employment, health care, and societal expectations are just a few of the ways this shows up. It’s important to remember that gender inequality affects everyone, but it has generally affected women and non-binary individuals more than men.
The Causes of Gender Inequality
Various social, cultural, economic, and political factors influence gender inequality, making it a complex and multifaceted issue. Here are some of the key causes:
Societal Norms:
The main factor that keeps gender inequality going is societal norms and standards. Gender roles that say women should care for others and men should work and make money can limit job options and keep unfair expectations alive.
Access to Education:
A major factor that keeps the inequality going is that girls and women don’t have as much access to good schools. In some societies, girls are not able to go to school because of things like a lack of facilities, traditional norms, and getting married young, among other things.
Workplace Discrimination:
Unfair hiring practices, unequal pay for the same work, and fewer chances to move up in your job are all examples of discrimination at work that contribute to gender inequality. Pay gaps between men and women in similar jobs and bias in hiring decisions based on gender.
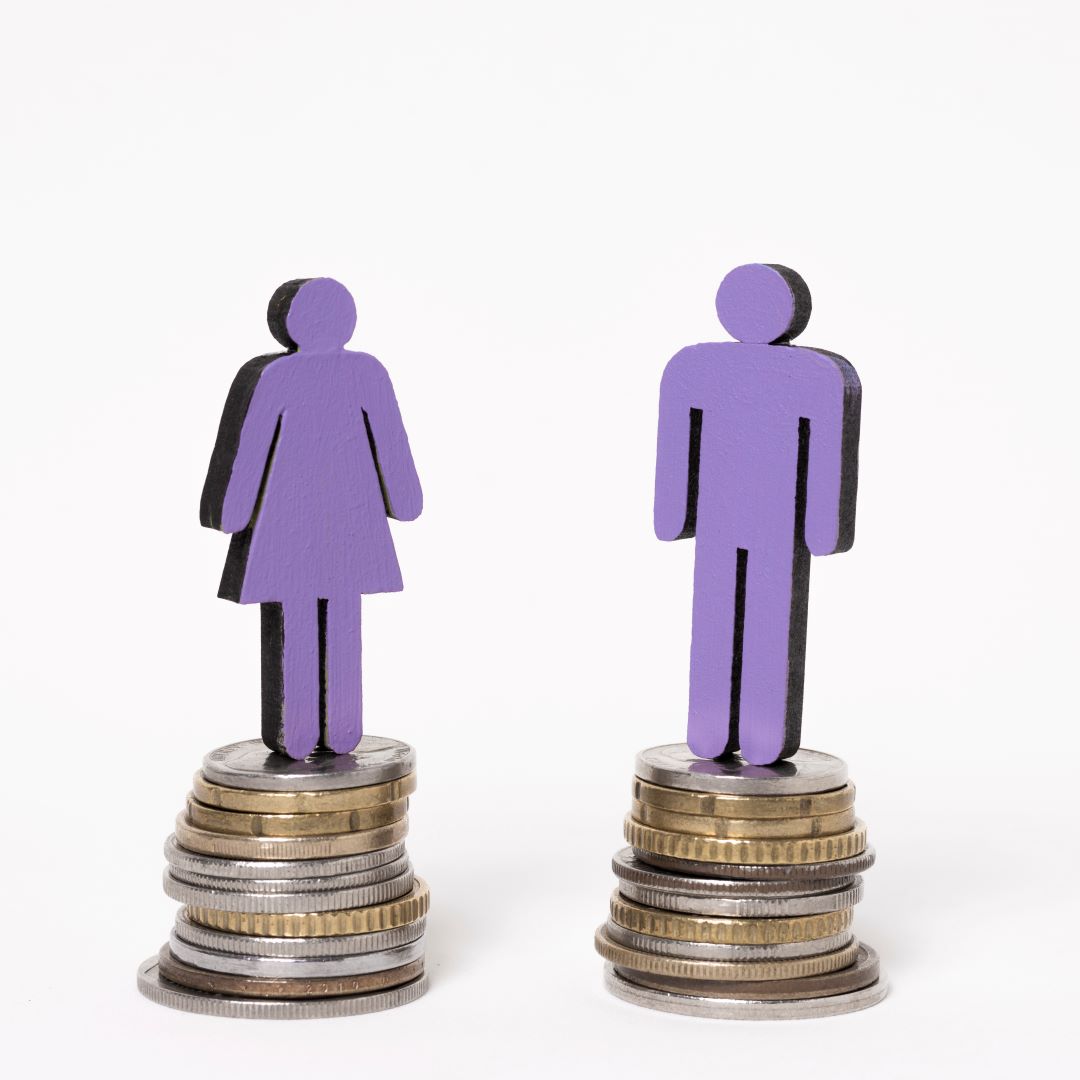
Wage Gap:
The wage gap highlights an economic inequality between men and women, resulting in women being paid less than men for the same work. Women are paid less than men for the same job with the same skills, highlighting the gender wage gap. This shows that there are systemic economic inequalities.
Lack of representation:
There aren’t many women in leadership roles in politics, business, or other decision-making bodies. This means that policies and choices may not meet the needs of all groups in the population.
Gender-Based Violence:
Violence against women, such as domestic abuse, harassment, and assault, is a big problem when it comes to equal rights for men and women. When there is domestic violence, sexual harassment, or an attack based on gender, it creates an atmosphere of fear. This makes power imbalances worse and keeps victims from reporting or getting help.
Distribution of Domestic Responsibilities:
According to traditional gender roles, women are usually in charge of caring for others and doing housework. Society’s assumptions that women should be the main carers can make them less likely to work and get ahead in their careers.
Legal and Policy Barriers:
Laws and rules that are biassed against women can make gender injustice permanent. Laws that discriminate against women, like those that limit their ability to own land or pass on their inheritance, can make inequality between men and women permanent.
Lack of Access to Healthcare:
In some areas, it may be hard for women to get good healthcare, which can cause health gaps between men and women. Women can have bad health effects if they can’t get access to reproductive health services like family planning and care for new mothers.
The media’s portrayal and stereotyping of gender can strengthen gender norms and standards. Media portrayals of gender roles that support societal norms and bias, like showing women in limited roles, can be harmful.
How to Tackle Inequality
Addressing gender inequality requires taking several important steps: Some of the most important steps include:
- Education: Teaching both men and women about equal rights for women and men is important for changing views and actions.
- Empowering women: Providing women with access to education, health care, and job chances can help give them more power.
- Challenging Gender Roles: We need to fight against the harmful assumptions and stereotypes that come with being a man or a woman.
- Supporting Laws and Policies: Policies and laws that support equal rights for men and women can help make society more fair and just.
- Advocating for Change: We can all do our part to fight for fair rights for men and women. We can do this by speaking out against discrimination, giving money to groups that work for gender equality, and voting for leaders who care about gender justice.
Gender inequality is a complex problem, but it is not one that we cannot solve. We can make a world where everyone, regardless of gender, has the chance to reach their full potential if we all work together.